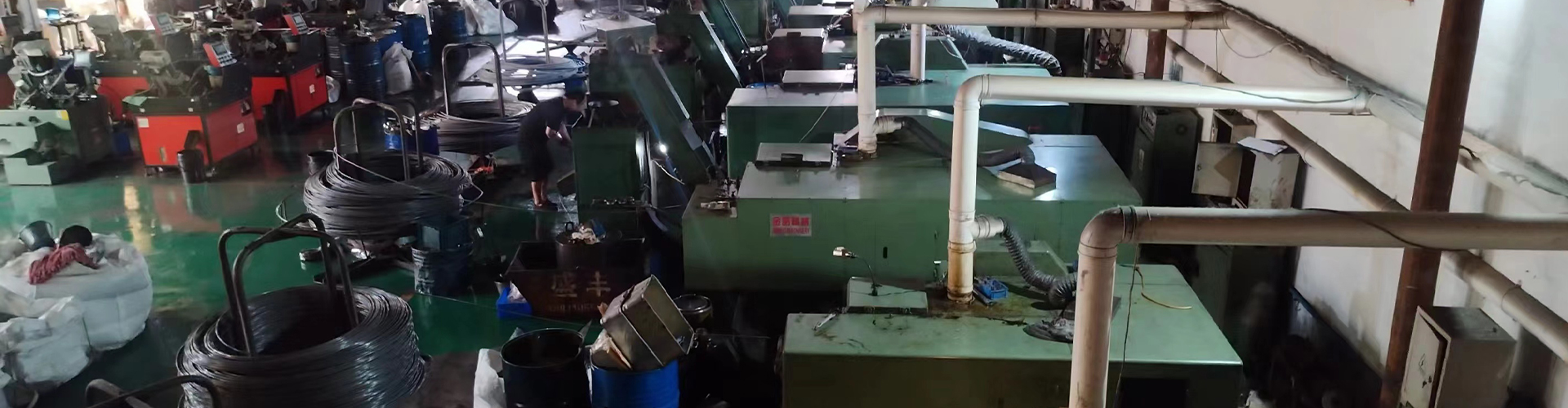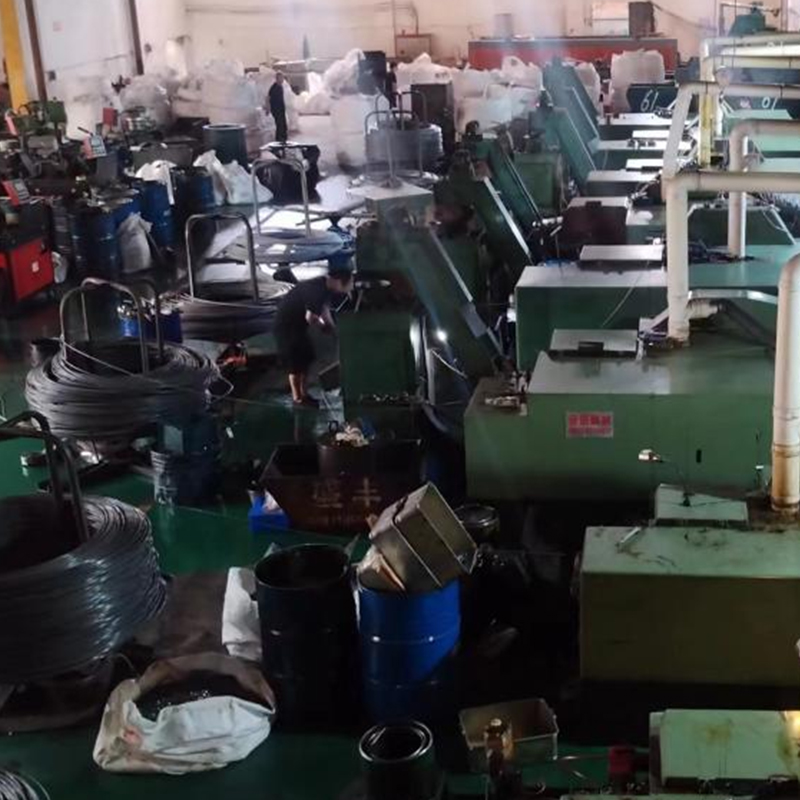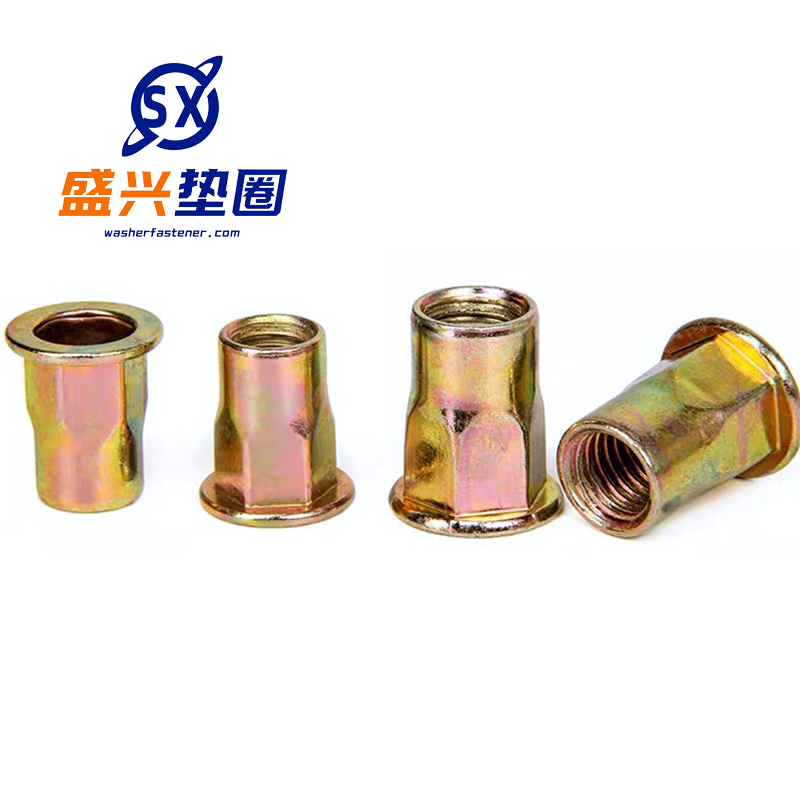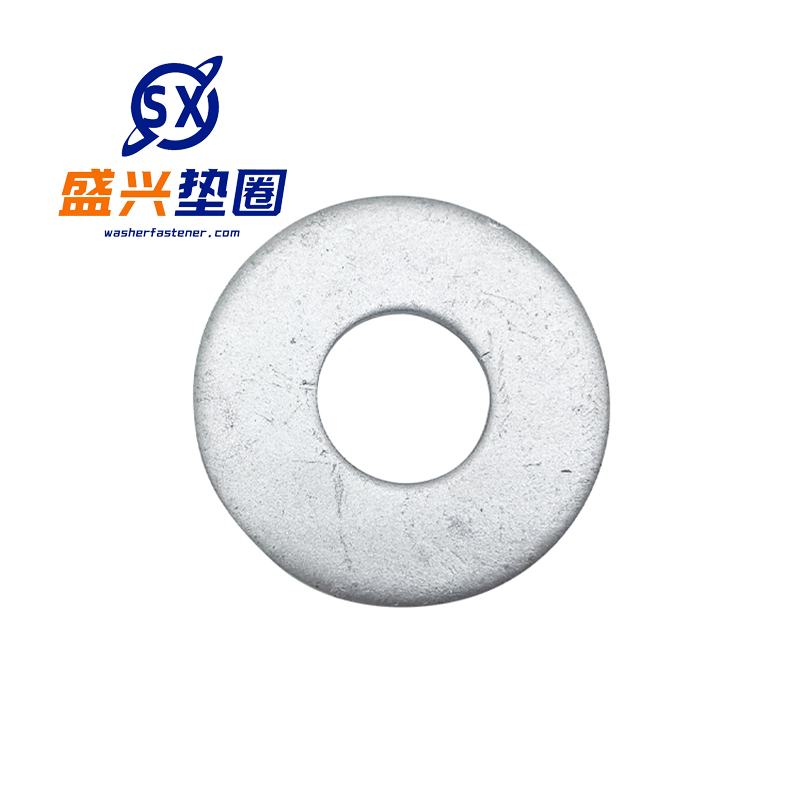
PRODUCTS
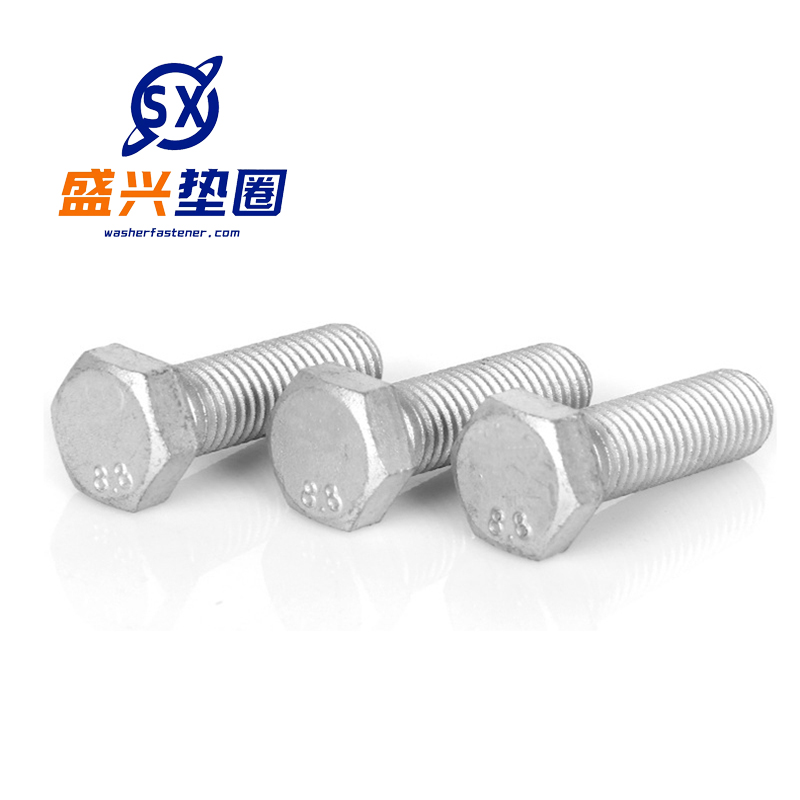
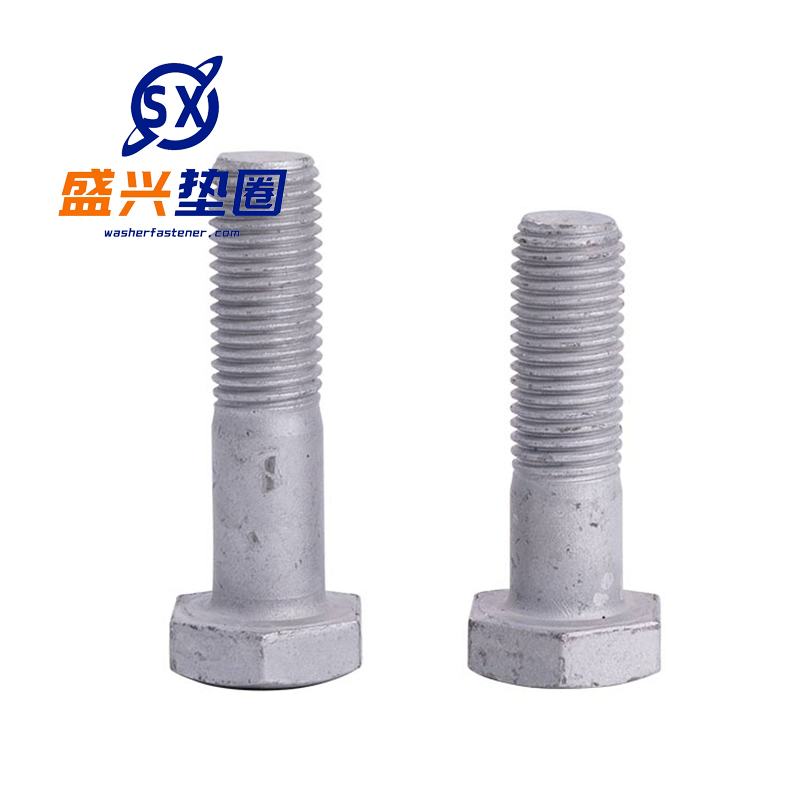
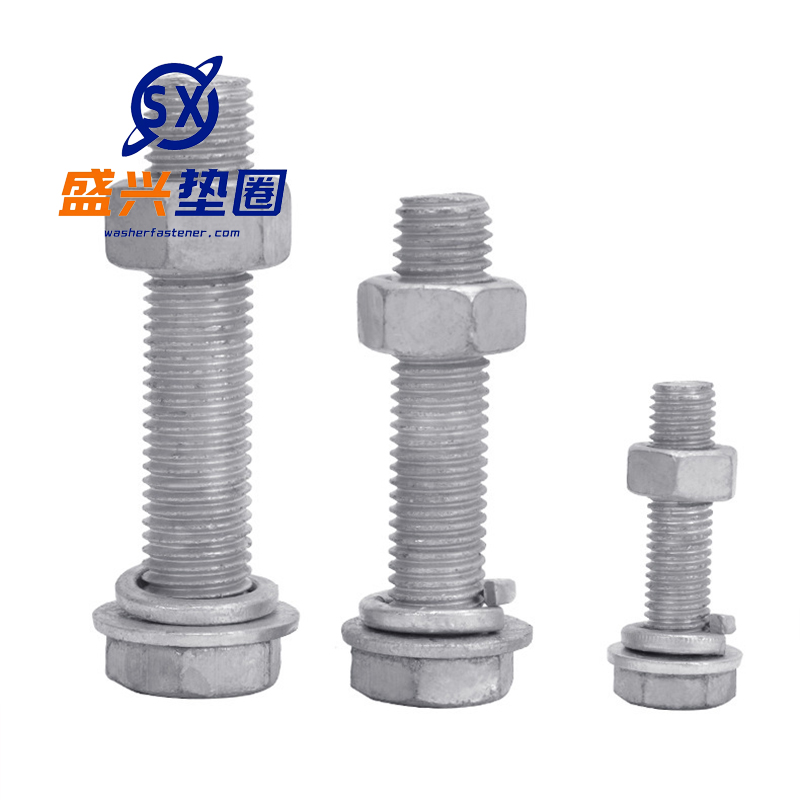
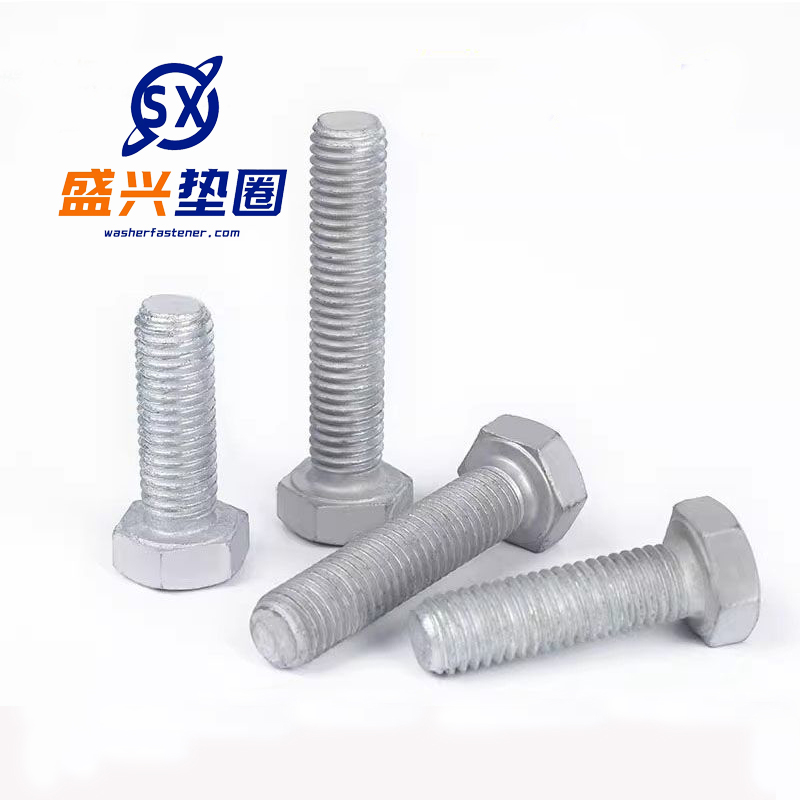
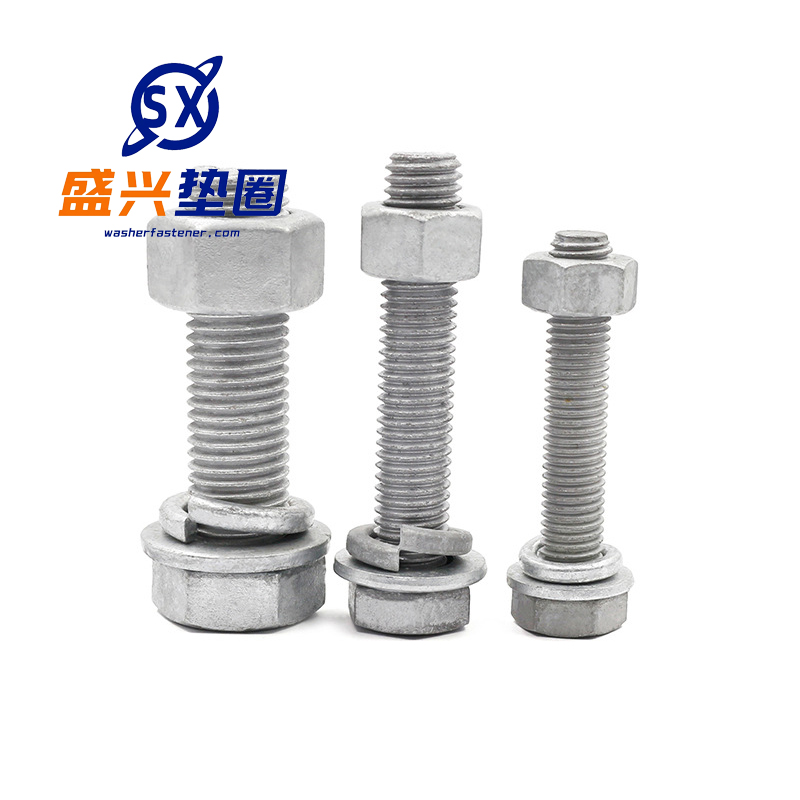
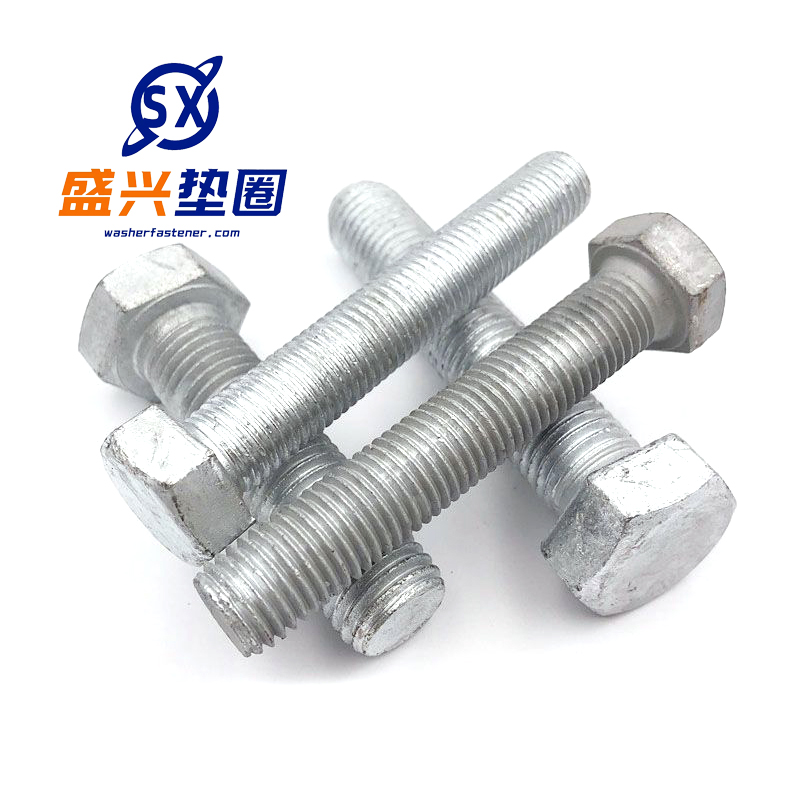
Hot-dip galvanized bolts
Function -Connection fastening: By cooperating with nuts and utilizing the mechanical principle of threads, two or more components can be tightly connected and fixed together, capable of withstanding various loads such as tension and pressure, ensuring the stability and reliability of the conn...
Description
marker
Function
-Connection fastening: By cooperating with nuts and utilizing the mechanical principle of threads, two or more components can be tightly connected and fixed together, capable of withstanding various loads such as tension and pressure, ensuring the stability and reliability of the connection structure.
-Corrosion prevention: The hot-dip galvanized layer can form a protective film of zinc iron alloy on the surface of the bolt, which has good chemical stability and can effectively prevent the corrosion of the bolt substrate by substances such as oxygen, moisture, acid and alkali salts in the atmosphere, extending the service life of the bolt.
-Wear resistance: The hot-dip galvanized layer increases the surface hardness of the bolt, reducing the wear caused by contact with other components during assembly and use, ensuring the dimensional accuracy and performance of the bolt, and enabling it to be reused multiple times.
Purpose
-In the field of architecture: used for connecting steel structures in building structures, such as the connection nodes between steel beams and steel columns; It is also used for fixing embedded parts in concrete structures, installing building curtain walls, and installing glass curtain walls in large commercial buildings.
-Power engineering: used for the connection and fixation of various components of transmission towers in the construction of transmission lines; In the substation, it is used for the installation and fixation of electrical equipment, such as transformers, switchgear, etc.
-Mechanical manufacturing: The manufacturing and assembly of various types of mechanical equipment cannot do without hot-dip galvanized bolts, such as in machine tools, industrial robots, agricultural machinery and other equipment, used to connect various mechanical components and ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
-Automobile manufacturing: The assembly of the engine, chassis, body and other parts of the car requires the use of hot-dip galvanized bolts, such as the assembly of the engine cylinder block, the connection of the chassis suspension system, and the fixation of the body shell.
-Bridge engineering: Whether it is highway bridges or railway bridges, hot-dip galvanized bolts are used for connecting bridge steel structures, fixing bridge supports, and installing bridge ancillary facilities, ensuring the structural safety and stability of bridges.





















